Autonomous Maintenance: 7 Steps to Successfully Implement
Autonomous maintenance is the first pillar of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). It is a way to provide your operators with the tools, including digital, always-updated work procedures, they need to perform maintenance tasks on their own equipment – emphasizing proactive and preventative maintenance. By giving machine operators the means to carry out part of the maintenance themselves, it leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
What is autonomous maintenance? How do you implement it? And, what are the benefits? If you want to lower your maintenance costs and increase efficiency, keep reading.
- What Is Autonomous Maintenance?
- What Are the Benefits of Autonomous Maintenance?
- Leverage Connected Worker To Implement Autonomous Maintenance
What Is Autonomous Maintenance?
Autonomous maintenance is a method in manufacturing that gives machine operators the responsibility for basic maintenance tasks, rather than relying on dedicated maintenance technicians. This core principle of TPM gives operators more control and authority, and allows maintenance personnel to focus on more complex maintenance work.
In some instances, operators run machines until they break or are due for maintenance, at which point they hand them over to the maintenance department (check out these interesting maintenance stats). Autonomous maintenance, on the other hand, allows machine operators to perform minor maintenance tasks, such as: lubrication, bolt tightening, cleaning, safety checks and inspections. Operators are the eyes and ears on the ground – the first line of defense to prevent breakdowns.
Autonomous maintenance follows two key principles:
- Prevent equipment deterioration through proper operation
- Get machines to “like new” standard of clean and keep them there
The primary goal of TPM is to improve your overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
By starting with autonomous maintenance, you’re relieving maintenance staff from having to worry about mundane maintenance tasks.
In turn, allowing machine operators to tackle these simple maintenance inspections – setting you up for success by maximizing OEE, through reducing the number of breakdowns and equipment failures.
What Are the Benefits of Autonomous Maintenance?

- Lower labor costs – Because operators are next to their machine at all times, this completely eliminates inefficiencies related to travel and waiting time for a maintenance technician to come on site.
- Verify equipment is properly cleaned and lubricated – When a maintenance technician is overseeing a big repair, simple tasks like cleaning and lubrication are often overlooked. But with autonomous maintenance, operators ensure these simple tasks are carried out.
- Detect issues before they get worse – Because operators work so closely with their machines, they have their finger on the pulse of the equipment they oversee. This means they are able to recognize early on, any signs of equipment malfunctioning and take the appropriate steps to address it.
- Free up maintenance personnel, so they can tend to more critical issues – They can plan and prioritize their specialized skills to higher-level and more complex equipment related issues.
- Improve team cohesiveness – By increasing employee participation, you’re creating a “we maintain” versus a traditional “I use” mindset. This fits directly within the pillars of TPM.
- Improve overall safety – Because operators are continually tending to the upkeep of machinery, there are likely fewer injuries because the surrounding work areas are no longer cluttered with tools and debris.
Leverage Connected Worker® from Parsable To Implement Autonomous Maintenance
When carried out correctly, everyone reaps the benefits of autonomous maintenance. Operators develop additional technical skills, maintenance technicians have more time to focus on complex tasks and your overall operations are on a path to operational efficiency.
Connected Worker plays a vital role in ensuring autonomous maintenance is consistently and accurately carried out across your organization. You can create a digital workflow experience in just a few minutes.
The easy-to-use content authoring tool makes the move from paper to digital as painless as possible.
A truly connected worker is always connected to the information they need to successfully complete their maintenance tasks. This includes forms and checklists, standard work instructions and operating procedures, even quick and easily digestible training or lessons accessible on demand.
There are seven basic steps to help successfully implement autonomous maintenance, and here’s how technology solutions can help with that:
1. Increase Operator Knowledge
In order to empower your operators, you must first teach them about the machines they’re operating on. They need to know the ins and outs of their machines. This involves becoming familiar with the technical details of how the machines’ components work and equipment-related issues. You must train them to identify abnormalities, fix abnormalities, set optimum equipment conditions and detect deviations from optimum performance. All of this can be carried out by creating digital training lessons within Parsable.
The best time to learn is before you need to know. The second best time is right when you need to know. Through the Parsable platform, operators can quickly access one-point lessons and interactive standard operating procedures (SOPs) through an easy-to-use mobile app, which lets them get the information they need, when they need it wherever they are on the factory floor. To further simplify things, you can create QR codes that launch the necessary resource so that operators spend less time searching for how-to guides and focus on the task at hand. What was once a lengthy onboarding time or dedicated time off the floor is now as simple as grab, scan and learn.
2. Initial Machine Cleaning and Inspection
Once you’ve trained your operators, they are now capable of performing inspections and cleanings. This step involves getting equipment to a place where it’s almost “like new,” to restore it to its full performance and keep it at an optimal condition. Your team will be looking for: leaks, loose bolts, proper lubrication, cracks, contamination, removal of dust and dirt, unusual sounds or smells, and heat. If operators run into a problem, they can easily alert and collaborate with other departments to take action against process deviations within Parsable.
After accessing the know-how, operators can get the tasks done. A classic example is an interactive digital checklist operators can complete through the Parsable app on their smartphone or company-provided device. Solutions like Parsable guide operators through each task, providing information on what needs to be done, best practices and walkthroughs for in-the-moment reminders, and control points to capture and document the details of the task. A common method used by many leading manufacturers is to document the before with a few pics and a video, as well as the after. Content like photos and videos become invaluable tools for improving compliance and conducting root-cause analyses.
3. Remove Causes of Contamination
Now that the cleaning process is complete, you want to make sure it stays that way. To ensure equipment doesn’t deteriorate, allow your operators to contain contamination. This starts by promoting good housekeeping and cleaning habits, using sealing methods and machine covers, and promoting a culture of cleanliness.
Safety is of the utmost importance. Cleaning a machine while it’s still running is extremely dangerous, and should be avoided at all costs. Provide your team with mobile step-by-step instructions on how to carry out lockout/tagout (LOTO). This is a necessary requirement in order for operators to eliminate contamination safely.
Identifying the causes of contamination takes some analysis – some root cause analysis to be exact. The data captured through Parsable is a critical component to an investigation. Instead of relying on paperwork, which may or may not have been pencil whipped, photos and videos mentioned in the previous section help your team to identify areas of interest. In addition, the data detailing who did what, when and the result empower teams to quickly pinpoint problems, which means solutions are identified more quickly. And, because your team can assign corrective actions through Parsable, you’re able to tackle what was previously a fragmented process with a simple and intuitive workflow, reducing time spent on non-value added activities and maximizing time spent on improving operations.
4. Develop Standards for Lubrication and Inspection
In order to reinforce and uphold what operators have learned so far, it’s important to document and have a digital record of standards on cleaning, inspecting and lubricating.
Digital checklists provide a simple way to drive consistency and compliance across these steps.
That way, operators have a point of reference and guide on what and how components should be cleaned and lubricated.
As these checklists are completed within Parsable, data is captured – data on who did what, when and the result. These data points help to create a crystal-clear picture of current-day operations. This is important because it’s now easier to quickly identify deviations from standards and the impacts those deviations had on production, quality or even safety. These deviations could represent institutional knowledge not reflected in SOPs, which means your team now has the data necessary to improve SOPs, one-point lessons and more with data-backed best practices – that would have otherwise been missed. This is critical for upskilling new workers and shortening the time it typically takes for new operators to become experts.
5. Inspection and Monitoring
Operators’ maintenance duties can be scheduled and tracked. Within Parsable’s mobile app, operators can make sure to follow a checklist that requires them to: check lubrication levels, locate leaks, tighten bolts, look for mechanical issues like cracks or wear. And as a manager, you can easily verify compliance and completion rates.
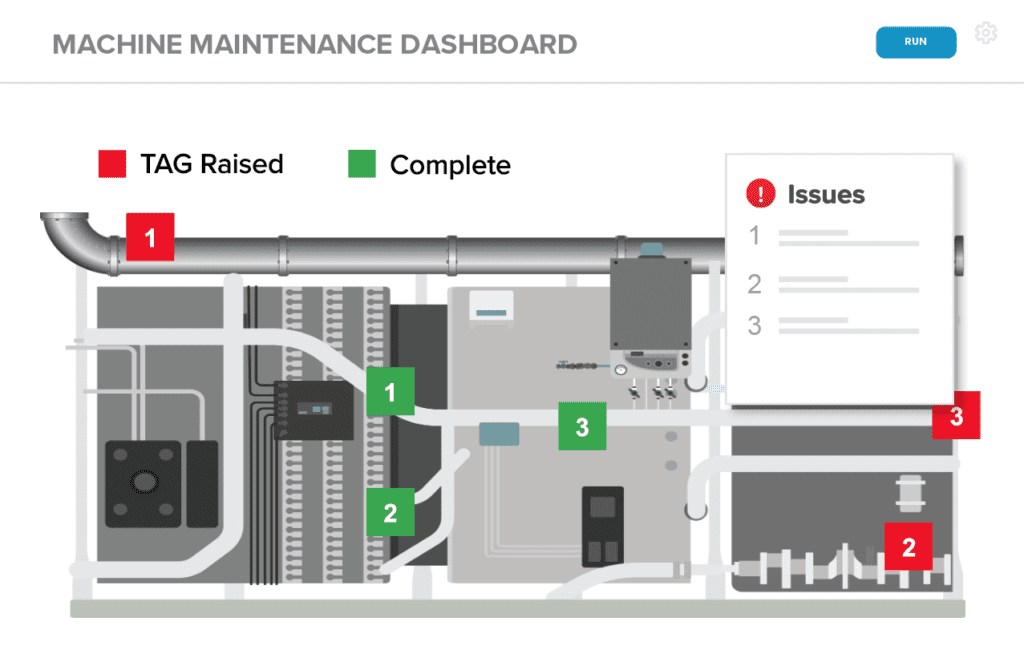
Tackling compliance alone can lead to big gains for your manufacturing operation. Pencil whipping plagues the frontline; it’s more reflective of an operation than of an operator. The visibility and traceability gained through the real-time digital experience made available through Parsable gives supervisors what they need to quickly track progress, get updates, and understand what still needs to get done. This means preventative maintenance tasks won’t fall through the cracks. Supervisors can check all active tasks for their operators and check in, even while remote. And for operators, preventative maintenance tasks can be structured, scheduled and started automatically, which helps people prioritize.
6. Standardize Visual Maintenance
Taking steps to make equipment more visual is important. What does that mean, exactly? For example, this could include identifying the flow of fluids in pipes, replacing opaque covers with transparent ones, labelling the open and close direction on levers and valves, and developing a tag system. These visual cues make things more obvious, allowing for a quicker inspection.
In addition, operators directly benefit from visual improvements, making sure they’re safely and efficiently completing an assigned task. Text-based work instructions with a few outdated pictures scattered throughout are less likely to be reviewed and consumed, especially when most people are used to a simpler experience in their personal lives. Today’s supporting resources require visual resources, like videos and gifs, to help operators quickly understand what to look for and where to look for it. Plus, these visual mediums make it easier for non-native speakers to overcome any language barriers that are further complicated by text-heavy training resources. This is a key reason why Parsable makes it easy for subject matter experts and process owners to embed digital media in-line with tasks.
7. Strive for Continuous Improvement
It’s important to take a step back once in a while and evaluate the standards and procedures you’ve created, to see where there is room for improvement. Continuous improvement is one of the other pillars of TPM – looking for ways to incrementally improve your autonomous maintenance processes.
We’ve covered a few ways of driving improvement in the other steps, but one way we’ve yet to highlight is the voice of the operator. It can sometimes be easy for managers and continuous improvement teams to overlook the most important asset in a factory: the people staffing the lines. While data captured through Parsable is critical in identifying new opportunities for improvement, giving workers a seamless way to report issues, suggest improvements, and track their own impact helps organizations capture what is so frequently overlooked – the creativity of the people who spend day in and day out working with the machines, products and processes at your factory.
Far too often, workers come to the conclusion that no one is listening. As a result, workers stop reporting issues or sharing their ideas. These unreported issues and ideas can be costly, leading to downtime (check out these interesting stats on downtime), lost time incidents and more – while allowing inefficiency to continue to persist.
Through Parsable, operators have a voice: a simple, digital tool which they can use to share what they see with managers and the people who have the power to implement change. When workers see their ideas considered and implemented, culture changes and ownership improves. That’s how you empower a workforce, and that’s a key requirement for sustaining autonomous maintenance.
Ready to revolutionize your maintenance workflows? Experience the power of Parsable’s Connected Worker® software firsthand and discover how our solution can streamline your maintenance operations!