What is Just in Time Manufacturing (JIT Manufacturing)?
Developing a near-flawless production strategy is essential to staying competitive in the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing. To stay competitive, companies often use continuous improvement in production processes to minimize inventories, uphold product quality, and prevent supply chain disruptions..
Continuous improvement relies on just-in-time manufacturing, which boosts efficiency in manufacturing processes. Here, we’ll clarify what a JIT system is, its origin, and how it boosts peak efficiency for manufacturing companies.
- What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing?
- History of Just-in-Time Manufacturing
- JIT 101
- Benefits of Just-in-Time Manufacturing
- Implementing the JIT methodology
- Potential Risks of JIT
- JIT Manufacturing and Connected Worker Software
What is Just-in-Time Manufacturing?
In simple terms, just-in-time manufacturing reorders manufacturing processes to streamline production. JIT involves changing raw material orders to match demand, preventing excess inventory and ensuring materials arrive when necessary.
If done correctly, manufacturing companies can produce goods and services on demand. This leads to significantly reduced storage costs and the potential for waste.
There benefits of JIT are many, but failing to institute the process correctly comes with risks, which we’ll explore below. So, to ensure success, first, understanding the history and basics of Kanban and lean manufacturing is essential.
Kanban 101 for Manufacturing
Kanban is a Japanese word that translates to “visual signal.”
Essentially, Kanban is when production managers create a visual chart with workflow columns, aka a Kanban board. The board outlines each step of the production process. The tool helps track progress by changing task cards to different statuses. These statuses include “To-Do,” “Past Due,” “In Process,” and “Complete.”
Project engineers developed Kanban in the 1940s, saying it helped to achieve four main outcomes.
- Visualize Work: Sort processes into stages and track each stage so all teams can visualize workflows
- Reduce Work In Progress: Visualizing task status allows manufacturing teams to better complete outstanding tasks and reduce unfinished work
- Optimize Workflows: By seeing each step, it’s easier to reorder workflows to improve efficiency
- Continuous Improvement: Visual processes germinate accurate and actionable measurements for KPIs like lead times, product quality, and wasted materials
Kanban offers immense value, providing a visible roadmap of an entire, often complex process. It works well because it’s a flexible process that enables companies to improve transparency, flexibility, focus, and productivity.
5 Lean Manufacturing Principles
Like Kanban, lean manufacturing is another branch of the continuous improvement philosophy tree. A lean mindset seeks to reduce production and response time. In practice, lean manufacturing sits on five pillars, also known as the 5S’s.
The 5S approach to lean manufacturing is as follows:
- Sort: Review tools, equipment, and processes to identify essentials and eliminate unnecessary items.
- Set In Order: Organize the manufacturing process by prioritizing elements and optimizing the layout for increased efficiency.
- Shine: Thoroughly clean and maintain the workspace and equipment so it’s easier to identify issues
- Standardize: After the initial cleaning, set up a calendar for routine maintenance and improvements
- Sustain: Continuously practice the first four steps to establish a culture of continuous improvement
History of Just-in-Time Manufacturing
The concept of just-in-time manufacturing is a product of post-World War II Japan. After the war, companies wanted to save money, work better, and get more money to use for their business. Lean manufacturing and JIT creators met economic needs by focusing on smaller productions and improving manufacturing processes.
Engineers at the Toyota Motor Corporation were among the first to develop theories behind lean manufacturing and JIT. Led by the renowned industrial engineer Taiichi Ohno, the company formed the Toyota Production System (TPS).
JIT 101
The TPS forged a few fundamental JIT principles. Chief among these was eliminating wasted raw materials. To succeed in this, companies aligned material shipments with production schedules, eliminating the need for storage.
To prevent mistakes in quality control and safety, JIT emphasized strict project management. Managers used the Kanban board to plan the workflow and track metrics to avoid missing any details.
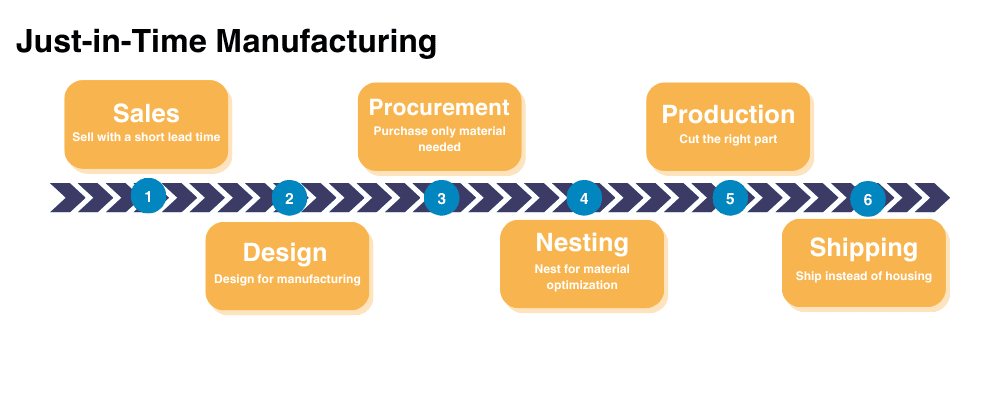
Benefits of Just-in-Time Manufacturing
People choose Just-in-time manufacturing because it improves productivity and production efficiency and has a proven track record. Some of the key benefits include:
- Cutting costs by reducing excess labor, overhead, and raw materials waste
- Improving efficiency and output by reducing space needed to complete production workflows
- Wider profit margins by reducing downtime and optimizing the amount of production for a manufacturing cycle
- Enhance customer satisfaction by eliminating work-in-process to increase product shipments and throughput
Implementing the JIT methodology
Any company considering implementing JIT correctly, needs to plan accordingly. As mentioned, establishing JIT is best done via Kanban project management. Whether digital or physical, mapping and visualizing every part of the process is crucial to prevent errors. In doing so, consider the following elements:
- Demand Forecasts
- Capacity Planning and Utilization
- Supply Chain Variables and Vendor Relationships
- Lead Times
First, get a solid grasp of these factors, then decide if JIT is the right philosophy to adopt right now. If you find severe risks or disorganization, fix core these core issues before jumping headfirst into JIT.
Potential Risks
Even when done right, JIT presents certain risks. For these reasons, thorough planning and project management is critical to reducing falling prey to potential pitfalls:
- Stock out: This happens when materials are not available when needed because of human planning errors. It can also occur due to unreliable supply chains.
- Supplier Dependency: Productions risk downtime if suppliers are unreliable or face raw materials shortages
- Planning: Careless planning leads to mistakes that harm profits and the company’s reputation.
JIT Manufacturing and Connected Worker Software
If you’re looking to nail down a high quality JIT approach, consider investing in connected worker software.
Parsable’s Connected Worker® Software digitizes frontline operations, equipping industrial leaders with a single software solution that increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improves sustainability. Parsable’s technology helps with 4.3M jobs, making $1.6T in revenue. It boosts throughput by 12% and improves OEE by 6% across 800+ sites.
Ready to revolutionize your operational workflows? Experience the power of Parsable’s Connected Worker® software firsthand and discover how our solution can streamline your operations by digitizing your frontline.