Tips for Good Hygiene Practices in Food Manufacturing
The food production process is rarely as simple as farm-to-table. The materials start at farms and travel to various places like factories, and processing plants before becoming final products.” Food producers must be diligent in eliminating the risk of cross-contamination at key control points throughout the production process.
We’ll explain what good hygiene practices in the food industry look like, and how these practices apply to each link in the food chain.
- What is Food Hygiene and Safety?
- What are the Benefits of Practicing Food Manufacturing Hygiene?
- Risks of Poor Food Manufacturing Hygiene
- Why It’s Important to Train For Food Hygiene
- Best Manufacturing Practices To Maintain Good Food Hygiene
- Tips to improve Good Hygiene Practices
- Connected Worker and Good Hygiene Practices
What is Food Hygiene and Safety?
Food hygiene and safety are complex subjects, and many food business operators get the two mixed up. Knowing the difference is critical to building processes that prioritize safety and customer protection.
What is Food Hygiene?
Food hygiene refers to the host of measures food manufacturing companies take to reduce food hazard risks, like contamination and spoilage.
For example, some food hygiene practices could be monitoring storage temperatures or imposing personal hygiene standards for employees, like hand washing practices.
What is Food Safety?
As opposed to hygiene, food safety is a larger umbrella. It applies to all aspects of the food production process rather than just instances pertaining to processing and handling. Compared to hygiene, food safety is more procedural, defined by a structured system of documentation, audits, and traceability.
Why is Food Hygiene and Safety Important?
Around 3,000 people in the United States die each year from food-related illnesses according to the CDC. Not only does this take a human toll, but it can destroy a company’s reputation diminishing profits, and can cause companywide collapse. However, many cases are preventable, and it begins with understanding the concepts behind food safety and hygiene.
What are the Benefits of Practicing Food Manufacturing Hygiene?
Food manufacturing hygiene is essential to give consumers confidence that your products meet their standards and are safe to eat. This increases customer loyalty and satisfaction and is great for a company’s reputation.
Ultimately, food hygiene prevents public health risks, which unfolds into many additional benefits, including:
- Job Security for Employees
- Lowered Turnover
- Lowered Risk of Litigation
- Prevention of Costly Fines
Additionally, a dedicated system that handles food processing and transportation manufacturing conducts and organizes safety at each stage of the process. Continuous improvements to the system drive lower food and product waste, crucially boosting profits and revenue..
Risks of Poor Food Manufacturing Hygiene
Just as there are benefits from thoughtful manufacturing practices and hygiene, there are risks that come with improper food hygiene.
The largest risk is cross-contamination, which can cause up to 250 types of food-related diseases and allergic reactions.
Not only is there a severe risk for allergens or disease, but once detected, federal mandates require product recalls. These recalls can completely halt operations which drain profits and result in lasting reputational damage.
There are also monetary risks, as failing to approach food hygiene correctly results in higher business costs. Poor safety practices often lead to higher insurance premiums, fines for non-compliance, and excess waste.
Why It’s Important to Train For Food Hygiene
Achieving proper food hygiene practices doesn’t happen overnight. It’s a systemic effort requiring every organizational member to understand what they can do to prevent food contamination.
Training employees in food hygiene best practices seems like a huge task, but it’s critical for success.
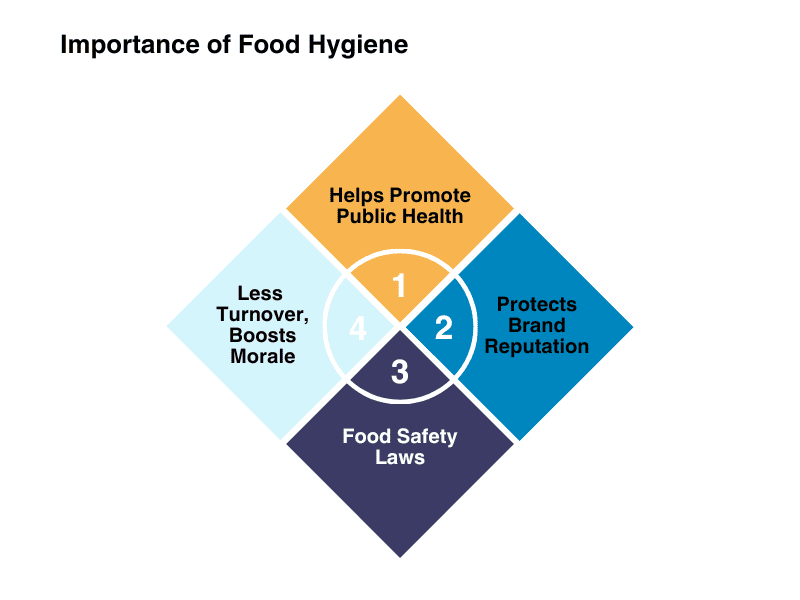
Helps Promote Public Health
Public health should always be the first priority with food handling. Training is useful for spreading awareness and ensuring everyone stays up-to-date on modern techniques and processes to avoid public health risks.
Protects Brand Reputation
Routine training establishes company-specific policies to ensure your brand’s reputation remains untarnished. Also, shared practices result in greater consistency, which improves customer satisfaction.
Food Safety Laws
Food safety laws change constantly. State and federal regulations must be communicated to frontline workers so they can keep workstations up to standard and shift procedures as the laws evolve.
Lowered Turnover and Increased Morale
With proper training, employees are less likely to make mistakes that cost them their jobs. Food safety training keeps workers on the same page. This results in more effective onboarding and allows experienced employees in training new hires to avoid costly mistakes that could cause termination.
Best Manufacturing Practices To Maintain Good Food Hygiene
Preventing food contamination is a multi-tiered approach. However, many clear, easy, and established practices exist for business operators to implement now that promote safety and hygiene practices.
Cleaning and Sanitizing of Surfaces
Prioritize cleaning and disinfection, especially when dealing with surfaces and products prone to disease and allergens, such as raw meats, peanuts, or shellfish.
Anytime employees work with such products or high-touch stations and surfaces, ensure strict cleaning and sanitization schedules, such as routine hand washing and cleaning with anti-bacterial soap and hot water.
Source Water
Test the source water to ensure it’s treated and free of contamination and pathogens.
Waste and Sewage
All waste and sewerage require proper storage and disposal techniques.
Product Packaging and Storage
It’s a good manufacturing practice to seal all food products properly to reduce the likelihood of cross-contamination during storage and transport. Likewise, all stored products require regular cleaning and inspection. For raw goods and perishables, the safest method is the first-in-first-out (FIFO) method.
Pest Control
Manufacturing and processing plants must regularly conduct inspections for pests that might contaminate food. If you discover pests, it’s crucial to have a direct plan for safely eradicating them..
Proper Holding And Preparation Temperature
Strict guidelines concerning storage temperatures are essential to prevent goods from spoiling or breeding bacteria. The same goes for preparation, as even a slightly incorrect preparation can expose products to conditions that create hygiene issues.
Transportation and Delivery
Monitor all goods during transport, storage, and delivery, ensuring they remain under safe, unhazardous conditions.
Food Sanitization Procedures
Thoroughly sanitize raw materials, especially produce, before packaging and shipment.
Employee Health
Form strict standards concerning personal hygiene for employees and management. Thes standards include policies like hair and facial hair coverings and orders for employees to remain home when ill.
Additionally, companies must provide employees with PPE, like masks, hairnets, shoe coverings, and tools to prevent disease transmissions.
Tips to improve GHP
Here are some top ways to build standard operating procedures (SOPs) to ensure your hygiene practices work.
Focus on SOP compliance and adherence
Emphasize the importance for staff to understand SOPs in full. Conduct training on a routine basis to close knowledge gaps concerning regulations.
Regular food safety audits, internal/external
Audits ensure food safety and that your operation remains in full compliance with existing legislation. There are two types of necessary audits: external third parties, and regular internal audits that critique existing processes to make them safer and more effective.
Have strong standard operating procedures
Effective hygiene practices require many SOPs that cover all your bases. This way, when questions arise, your team can reference SOPs.
Sanitation SOPs
These SOPs apply to all procedures concerning cleaning and disinfection, which include:
- Cleaning schedules
- Proper agents to use in different situations
- Explanations on surfaces, utensils, and equipment require the most intense sanitization
Food handling SOPs
Food handling SOPs explain proper methods for handling food, including:
- Storage techniques and guidelines
- Food prep and cooking instructions
- Temperature control and cooling requirements
HACCP-based SOPs
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) SOPs establish rules during processing and manufacturing to protect food from chemical and biological hazards.
Quality Control SOPs
These SOPs specify how to evaluate product quality at every stage, from analyzing raw materials to inspections right before shipment.
Regulatory compliance SOPs
Compliance SOPs outline what’s necessary to adhere to government mandates concerning issues like:
- Allergens
- Labeling
- Bookkeeping
Operational SOPs
These SOPs focus on constructing efficient workflows for processes like deliveries, shipping, managing inventory, and food preparation/storage.
Waste Management SOPs
The guidelines instruct employees on how to store and dispose of waste safely and according to regulations to limit the risk of contamination.
Recall SOPs
Provides protocol in instances of product recalls, which includes incident handling measures like pulling products from circulation and informing customers.
Pest Control SOPs
These SOPs include advice and guidelines on food storage, waste management, and sanitation guidelines for preventing pests. They also outline procedures for handling the discovery of rats, roaches, or other pests.
How to develop and implement effective SOPs for good hygiene practices
Creating SOPs that adapt and scale to business growth requires the following techniques.
Establish an SOP team
Put together a group of experts who can plan, manage, and update SOPs according to compliance mandates and optimize efforts to boost operational efficiency.
Conduct a thorough assessment
When creating SOPs, audit existing practices across each process stage to account for strengths and weaknesses.
Document clearly and concisely
Create clear, visual documents to outline all SOPs in the most effective way possible.
Train and educate employees
Conduct regular training whenever major changes to SOPs occur.
Review and update regularly
Update your SOPs and communicate updates with all your employees to keep information relevant and accessible.
Digital tools and technology
SOPs are complicated documents that frequently change, meaning they require fast, accurate tools to issue updates. Connected worker software is the best way to centralize SOP management and automate key tasks like audit alerts, deadlines, or mass communication.

Challenges in SOP compliance
Implementing SOPs isn’t simple. You must be aware of these common roadblocks as you build the safest food SOPs possible.
Develop and implementation
Robust SOPs require much time, energy, and thought. It’s much harder to accomplish effective change without the right digital tools to manage, update, and roll out these living documents.
Maintaining and updating
Regulatory and operational conditions always change. As they do, so do SOPs, which require the right tools that provide version control. This way, you can effectively manage and update documents with ease.
Compliance and enforcement
Audits are incredibly stressful and time-consuming, but if you fail to meet compliance the results can be catastrophic. However, keeping tack of compliance status and evolving regulations becomes much more straightforward with a dedicated connected worker software.
Parsable Connected Worker
Relying on a third party to manage your processes and principles of food hygiene is incredibly risky, and using paper processes for SOP management is cumbersome and prone to error.
Parsable’s Connected Worker® software is one of the market’s leading digital tools for creating, executing, and optimizing food hygiene SOPs. It digitizes your frontlines, prioritizing safety as a core principle, and allowing owners to create core documents and disseminate information to all workers. The software also records and automates safety analysis, promoting a culture of continuous improvement.
As a result, from the top down everyone is on the same page concerning safety and compliance, taking part in an environment that protects workers, customers, and businesses.
Want to learn more about the future of work? Read more about the approach that encompasses all of the solutions you’ll need to maximize efficiency, improve worker safety and create a higher standard of production quality.