What Is a Smart Factory? Manufacturing’s Future
These days, everything’s smart: smartphones, smart cars, smart homes, smartwatches, smart cat litter trays.
The smart craze is justified by the results, as connecting key devices to the internet provides users with safer, more powerful, and easier-to-use tools. However, smart technology doesn’t merely apply to standalone devices. Through the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing, enterprises can link thousands of devices to create an entire ecosystem of smart systems, tools, and processes. Then, these companies can uncover impactful insights through the power of big data analytics.
Now, entire factories use sensors to create smart networks. Such digital transformations use internet connectivity to leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence to automate their processes and analytics, building a culture of continuous improvement in the process.
Curious to know more about the smart factory? Below, we’ll explore the concepts behind smart factories, what it takes to create one, and the amazing benefits they provide.
- Smart Factory Overview
- Smart Factories for an Evolving World
- What Makes a Factory Smart?
- Benefits of a Smart Factory
- Smart Factory Technologies
- Smart Manufacturing’s Key Capabilities
- Becoming a Smart Manufacturer
Smart Factory Overview
Industry 4.0 is an important term driving the next generation of manufacturing. Experts break down the Industrial Revolution into four stages, including:
- Industry 1.0: mass production made possible by steam- and water-powered mechanisms
- Industry 2.0: introduction of assembly lines through the power of gas and electricity to improve mass production capabilities
- Industry 3.0: computers and communication devices allowing companies to harvest and analyze data, placing a focus on customer satisfaction rather than sheer production
Now, there’s Industry 4.0, defined by a more integrated use of the internet to power smart machines, technologies, and tools. Industry 4.0 technology crunches large amounts of data, facilitating automation and more informed insights.
Industry 4.0 technologies include:
- IoT
- Cloud computing
- AI and machine learning
- Augmented reality
These tech developments stand on the leading edge of the fourth industrial revolution. They’re critical to forming physical and digital processes that are more efficient, more cost-friendly, safer, and oriented to improve customer satisfaction.
Smart Factories for an Evolving World
As a public good, the internet is just over 30 years old, and the world is still learning to understand its full impact. As such, Industry 4.0 is still in its infancy.
However, one thing is evident: Adopting smart manufacturing tools is critical to staying afloat in the modern industrial landscape. A recent study showed that 86% of manufacturing executives think smart factories will drive their competitiveness throughout the next decade.
Now, all areas of the factory, from the shop floor to production systems, can be rigged with smart technology to establish greater resilience in the face of mounting supply chain disruptions and shortages.
What Makes a Factory Smart?
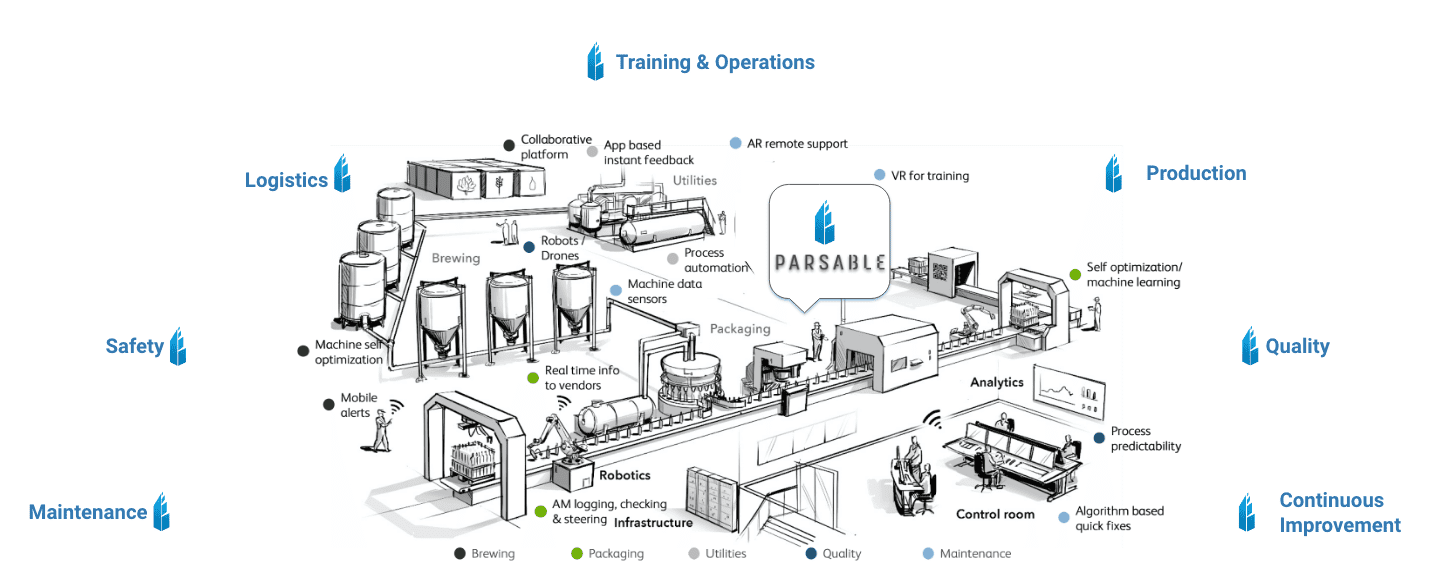
Ultimately, there’s no blueprint for forming a smart factory. It depends entirely on your unique circumstances. All that’s necessary is the latest digital technology, such as Parsable’s Connected Worker® mobile app, to connect people, processes, and machines.
The structure of a smart factory
While every smart factory looks different, transitioning a normal factory into a smart one relies on a structure that sits on three core pillars.
1. Data acquisition
Industry 4.0 technologies consolidate and integrate data across key systems. The first step to establishing a smart factory is finding the right technology to gather data across all of your workflows. For example, operations managers can place sensors on key industrial tools to gather metrics on performance, material waste, or downtime.
2. Data analysis
Another key element of the smart factory is its ability to merge real-time data with historical data to provide accurate recommendations for streamlining operations.
With potentially hundreds of datasets coming through, machine learning mechanisms rapidly sort the data. From there, they employ advanced analytics to offer action-oriented insights concerning issues like maintenance, logistics, or demand forecasts.
3. Automation
After the data collection and analysis, smart factories can self-optimize.
AI and machine learning are two enormous pieces of Industry 4.0. Using algorithms, they interpret data and take action without human intervention.
An example of this is machines that monitor historical and real-time demand. Factory automation also applies to machines that conduct predictive maintenance, which reduces downtime and repair costs.
Benefits of a Smart Factory
Industry 4.0 technologies are more available and affordable than ever, and many manufacturing companies now realize that even minor initiatives can lead to massive smart factory benefits.
Productivity and efficiency
Predictive analytics are one of the most impactful outcomes of Industry 4.0. Through more insightful analyses, businesses can avoid taking a reactive approach to underlying inefficiencies. Instead, through smart factory technology, they can peek into the future.
These developments lead to massive boosts in productivity and responsiveness. They minimize redundancies while maximizing the company’s ability to sustain or increase its current production levels without making costly investments in equipment and personnel.
Sustainability and safety
Industry 4.0 seeks to enhance more than just production quantity.
Now, consumers prioritize sustainability as a baseline requirement for their products. Smart factory technology allows companies to lock in practices that reduce waste and increase workplace safety. For example, IoT sensors are great for monitoring utility usage and carbon footprints, allowing companies to set goals and develop plans to meet consumers’ expectations and regulatory requirements.
Product quality and the customer experience
Customers’ preferences and expectations are subject to shifting trends.
Advanced analytics tools and cloud computing platforms allow companies to identify new consumer trends as they arise and shift their product development or marketing strategies to align with buyers’ needs.
Smart Factory Technologies
While technology isn’t the only factor at play in smart factories, it allows processes to become more scalable, reduce production times, and provide safer work environments.
Here are some of the most common solutions for launching your factory into the brave new world of Industry 4.0.
Sensors
IoT sensors are the heart of processing and using datasets. With the right sensors, analog machines can provide valuable insights that help lower costs, raise production levels, and enhance customer value.
Cloud computing
Cloud computing is the central storage unit through which all data flows. It abolishes the need for physical servers and connects factories, warehouses, and supply chains across a national or global digital network. This network, freed from physical constraints, leads to deeper insights that apply across entire workflows.
Big data analytics
Historically, processing data required immense human effort to sift through troves of data and link important insights.
Big data analytics speed up the process, automatically compiling datasets and scraping them for insights. Then, they generate clear, visual reports concerning solutions like preventative maintenance or predictive insights concerning seasonal demand and optimal work schedules.
Virtual and augmented reality
A factory’s efficiency relies on spatial awareness and optimizing layouts and inventories. Virtual and augmented reality can enhance your ability to analyze environmental conditions and spot areas for improvement to avoid stock-outs.
Digital twins
A digital twin is a virtual copy of a physical machine, process, or product. Factory managers can run tests on a digital twin to gain insights and run accelerated risk assessments to test things like production capacity. Overall, digital twins can significantly reduce time to market while enhancing your efficiency.
Smart Manufacturing’s Key Capabilities
Smart factories are critical to continuous improvement. However, properly integrating these technologies hinges on centralizing data-driven insights, analytics, and communication, which is best accomplished through a modern suite of tools, like with Parsable’s mobile-first approach.
Visibility
Big data, VR, AR, and digital twins all promote heightened insights across the manufacturing process. A connected worker platform provides a place to store insights, collaborate across teams, and share practices that promote efficiency, sustainability, and safety.
Prioritizing insights
Certain data-driven insights require greater urgency when it comes to integration. For example, if an IoT sensor uncovers a worker safety issue, it requires immediate attention before causing severe damage.
Connected worker software integrates all of your sensors and operational data, configuring reports to identify and prioritize trends. Then it communicates these insights to those with the power to enact meaningful change.
Resolution structure
Problem resolution works better with clear channels of communication and accountability. For example, shared digital communication is much more effective than paper documents. However, 81% of manufacturers still rely on paper-based processes for workplace instructions and procedures.
Centralized software allows management to map out processes and standardize workflows to institute an effective resolution structure from the top down.
Speed to value
Speed to value is a principle concerning how fast manufacturers can implement changes that bring customers greater value. With effective communication platforms, companies can take their data-driven insights and deliver more value at greater speeds.
Empowered employees
Employees are at their best when they have access to key insights. Connected worker software empowers employees by providing a central location to access critical data and training resources concerning workplace safety, product updates, and compliance.
Becoming a Smart Manufacturer
Interested in taking the leap to become a smart manufacturer? Here’s a general outline of what it takes to become one.
Strategy
Identify key areas of concern, such as production inefficiencies, downtime events, supply chain stoppages, and inventory stock-outs. Then, strategically select the smart technologies that best address your core issues.
Connectivity
Find ways to digitize your processes and equipment through IoT sensors.
System integration
Integrate all of your connected systems through cloud computing and connected worker tools to gain an overview of the entire manufacturing process.
Advanced analytics
After connecting and integrating your devices, employ big data tools to unearth predictive and prescriptive insights. For example, on the factory floor, sensor data can help you predict when a machine needs repairs, and connected worker software can alert managers to take action before any issues escalate.
Optimization
Use action-oriented data to boost your productivity and optimize your workflows, schedules, inventory levels, and supply chain efficiency. Continue re-evaluating each step of the process to optimize your smart factory approach as you commit to continuous improvement.
Want to learn more about the future of work? Read more about the approach that encompasses all of the solutions you’ll need to maximize efficiency, improve worker safety and create a higher standard of production quality.